For the titration of a weak acid with a strong base, the pH curve is initially acidic and has a basic equivalence point (pH > 7). The section of curve between the initial point and the equivalence point is known as the buffer region. At the half-equivalence point, the concentrations of the buffer components are equal, resulting in pH = pKₐ.
Solved Select Strong Acid as the analyte and Phenolphthalein | Chegg.com
Select Weak Acid as the analyte in the titration interactive. Determine the pK, of this weak acid. Analyte, 25.0 ml Strong Acid, 1.0… Indicator Phenolphthalein PK, = 9.4 Concentration (M) 0.33 0.33 0 0.00 но онх Titration Curve Concentration Chart Titrant: Strong Base, 10 M MOH – 50.0 mL + Not the question you’re looking for?

Source Image: numerade.com
Download Image
Indicator: For the purposes of this tutorial, it’s good enough to know that an indicator is a weak acid or base that is added to the analyte solution, and it changes color when the equivalence point is reached i.e. the point at which the amount of titrant added is just enough to completely neutralize the analyte solution.The point at which the indicator changes color is called the endpoint.
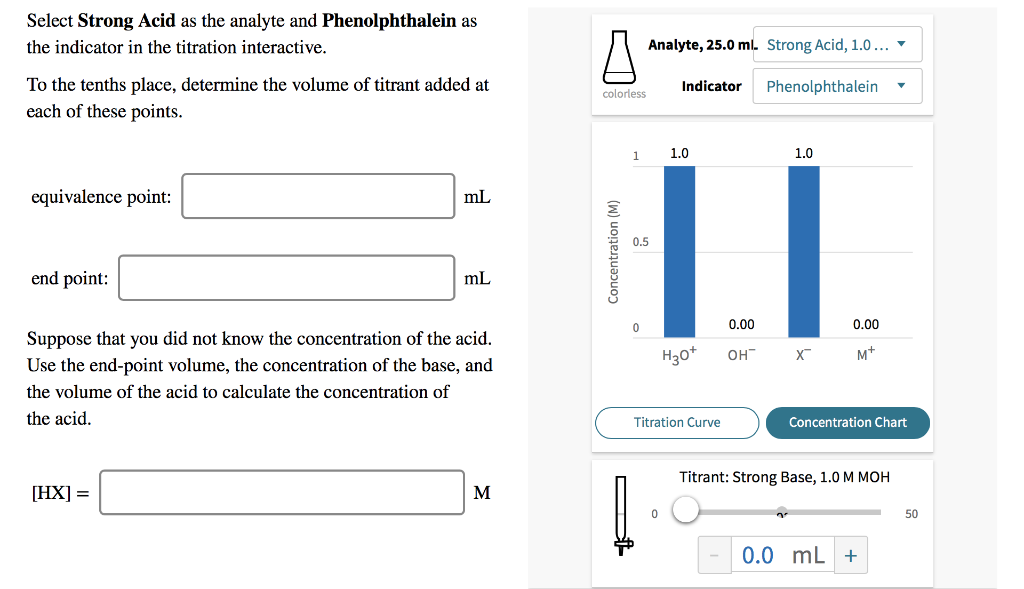
Source Image: chegg.com
Download Image
How does the graph of pH meter titration look? – Quora Question: Select Weak Acid as the analyte in the titration interactive. Determine the pKof this weak acid. A. Analyte, 25.0 ml. Strong Acid, 1.0…. Indicator No Indicator colorless 14 pk = 7 Hd pH=0.00 0 50 25 Titrant Added im Titration Curve Concentration Chart Titrant: Strong Base, 10 M MOH 0 0.0 mL + Show transcribed image text

Source Image: numerade.com
Download Image
Select Weak Acid As The Analyte In The Titration Interactive
Question: Select Weak Acid as the analyte in the titration interactive. Determine the pKof this weak acid. A. Analyte, 25.0 ml. Strong Acid, 1.0…. Indicator No Indicator colorless 14 pk = 7 Hd pH=0.00 0 50 25 Titrant Added im Titration Curve Concentration Chart Titrant: Strong Base, 10 M MOH 0 0.0 mL + Show transcribed image text Oct 30, 2022There are four parts to the titration curve of a weak acid (analyte) with a strong base (titrant). Buffer Equation (Henderson Hasselbach Eq.) Figure17.3.3: Four parts of the titration curve for a weak acid being titrated with a strong base. Notice that two parts are points (1 & 3) and two parts are regions (2 & 4).
SOLVED: Identify each type of titration curve: Note that the analyte is stated first, followed by the titrant. Drag each graph to the appropriate bin. View Available Hint(s) Reset Help mL of
Video transcript. – Here we have a titration curve for the titration of 50 milliliters of 0.200 molar of acetic acid, and to our acetic solution we’re adding some 0.0500 molar sodium hydroxide. So once again we’re putting pH in the Y axis, and down here in the X axis is the milliliters of base that we are adding. SOLVED: Student Exploration: Titration Vocabulary: acid, analyte, base, dissociate, equivalence point; indicator, litmus paper, molarity, neutralize, pH, strong acid, strong base, titrant, titration, titration curve; weak acid, weak base Prior …
Source Image: numerade.com
Download Image
SOLVED: Select Weak Acid as the analyte in the titration interactive. Determine the pKa of this weak acid. Analyte: 25.0 mL Strong Acid, 1.0 M Indicator: No Indicator pKa: 5.32 Video transcript. – Here we have a titration curve for the titration of 50 milliliters of 0.200 molar of acetic acid, and to our acetic solution we’re adding some 0.0500 molar sodium hydroxide. So once again we’re putting pH in the Y axis, and down here in the X axis is the milliliters of base that we are adding.

Source Image: numerade.com
Download Image
Solved Select Strong Acid as the analyte and Phenolphthalein | Chegg.com For the titration of a weak acid with a strong base, the pH curve is initially acidic and has a basic equivalence point (pH > 7). The section of curve between the initial point and the equivalence point is known as the buffer region. At the half-equivalence point, the concentrations of the buffer components are equal, resulting in pH = pKₐ.
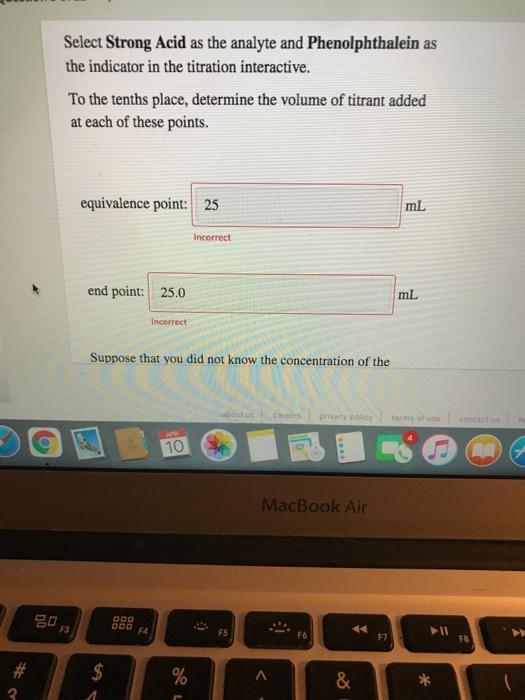
Source Image: chegg.com
Download Image
How does the graph of pH meter titration look? – Quora Indicator: For the purposes of this tutorial, it’s good enough to know that an indicator is a weak acid or base that is added to the analyte solution, and it changes color when the equivalence point is reached i.e. the point at which the amount of titrant added is just enough to completely neutralize the analyte solution.The point at which the indicator changes color is called the endpoint.
Source Image: quora.com
Download Image
SOLUTION: Titration Student Exploration Worksheet – Studypool Let us consider the titration of 25.0 mL of 0.100 M acetic acid (a weak acid) with 0.100 M sodium hydroxide and compare the titration curve with that of the strong acid . Figure 1. The titration curve for the titration of 25.00 mL of 0.100 M CH 3 COOH (weak acid) with 0.100 M NaOH (strong base) has an equivalence point of 8.72 pH.

Source Image: studypool.com
Download Image
Titrations of Weak & Strong Acids & Bases – Video & Lesson Transcript | Study.com Question: Select Weak Acid as the analyte in the titration interactive. Determine the pKof this weak acid. A. Analyte, 25.0 ml. Strong Acid, 1.0…. Indicator No Indicator colorless 14 pk = 7 Hd pH=0.00 0 50 25 Titrant Added im Titration Curve Concentration Chart Titrant: Strong Base, 10 M MOH 0 0.0 mL + Show transcribed image text

Source Image: study.com
Download Image
Solved Select Weak Acid as the analyte in the titration | Chegg.com Oct 30, 2022There are four parts to the titration curve of a weak acid (analyte) with a strong base (titrant). Buffer Equation (Henderson Hasselbach Eq.) Figure17.3.3: Four parts of the titration curve for a weak acid being titrated with a strong base. Notice that two parts are points (1 & 3) and two parts are regions (2 & 4).
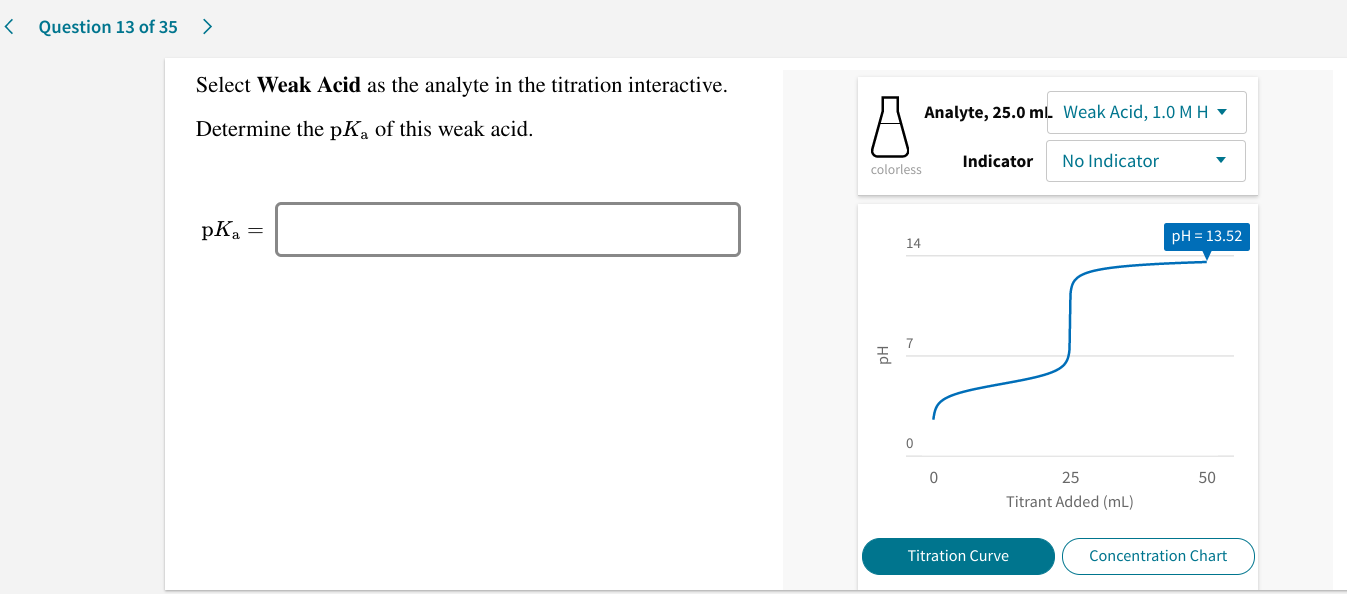
Source Image: chegg.com
Download Image
SOLVED: Select Weak Acid as the analyte in the titration interactive. Determine the pKa of this weak acid. Analyte: 25.0 mL Strong Acid, 1.0 M Indicator: No Indicator pKa: 5.32
Solved Select Weak Acid as the analyte in the titration | Chegg.com Select Weak Acid as the analyte in the titration interactive. Determine the pK, of this weak acid. Analyte, 25.0 ml Strong Acid, 1.0… Indicator Phenolphthalein PK, = 9.4 Concentration (M) 0.33 0.33 0 0.00 но онх Titration Curve Concentration Chart Titrant: Strong Base, 10 M MOH – 50.0 mL + Not the question you’re looking for?
How does the graph of pH meter titration look? – Quora Titrations of Weak & Strong Acids & Bases – Video & Lesson Transcript | Study.com Let us consider the titration of 25.0 mL of 0.100 M acetic acid (a weak acid) with 0.100 M sodium hydroxide and compare the titration curve with that of the strong acid . Figure 1. The titration curve for the titration of 25.00 mL of 0.100 M CH 3 COOH (weak acid) with 0.100 M NaOH (strong base) has an equivalence point of 8.72 pH.